Bio Solubilization of Eppawala Rock Phosphate (ERP) by Fungal-Bacterial Biofilm Action and its Effect on Crop Enhancement of Chili (Capsicum annuum)
##plugins.themes.academic_pro.article.main##
Abstract
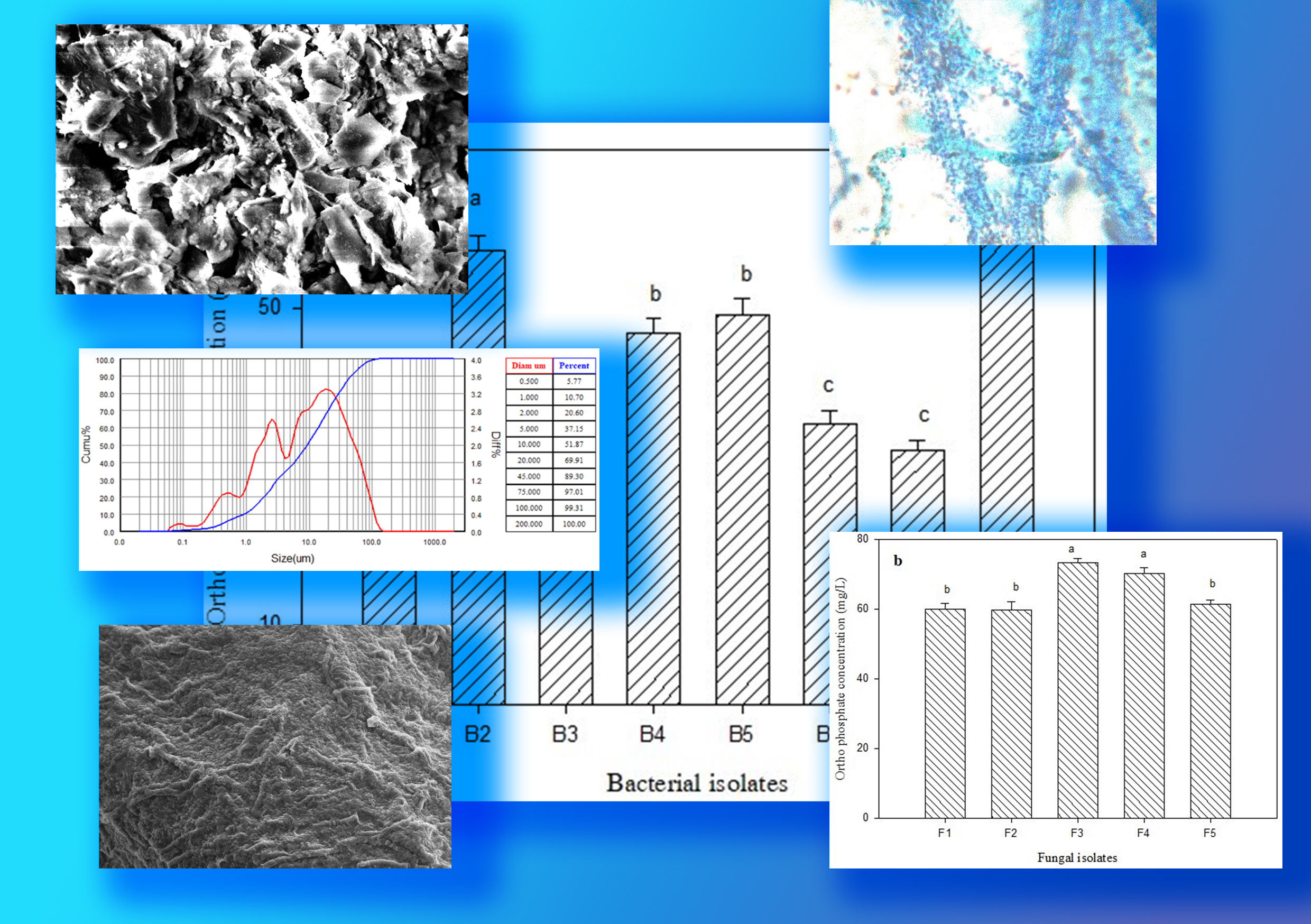
Eppawala rock phosphate (ERP) has potential as a substitute for Triple Super Phosphate (TSP) due to its phosphorus content, but its low solubility limits its application. Recent research indicates that biofilms could enhance ERP's effectiveness by enhancing its solubility. This study evaluated the effectiveness of ERP solubilized through fungal bacterial biofilms (FBBs) and their impact on chili (Capsicum annuum) crop enhancement. Fungi and bacteria were isolated, screened for phosphate solubilization and develop FBBs, which were then tested for their phosphate-solubilizing ability with powdered ERP. The best FBBs was evaluated for its phosphate-solubilization with different CF combinations using a pot experiment with chili crop. The best biofilm, BF3, composed of Brevibacillus brevis and Penicillium polonicum, showed significantly greater phosphate solubilization capacity (P < 0.05), and the lowest medium pH. FTIR analysis of the biofilm-treated and untreated ERP samples showed significant changes in the intensity and positions of the phosphate bands, confirming their involvement in phosphate solubilization. Combining FBBs with ERP, especially when pretreated, significantly (P < 0.05) enhanced chlorophyll content, fresh weight and number of fruits of chili plants. It can be concluded that biofilm enriched ERP performs better compared to the DOA recommended TSP dosage in chili cultivation under controlled conditions.