Antagonistic Yeast-based Biocontrol against Penicillium sp. Spoilage for Prolonging the Shelf Life of Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum)
##plugins.themes.academic_pro.article.main##
Abstract
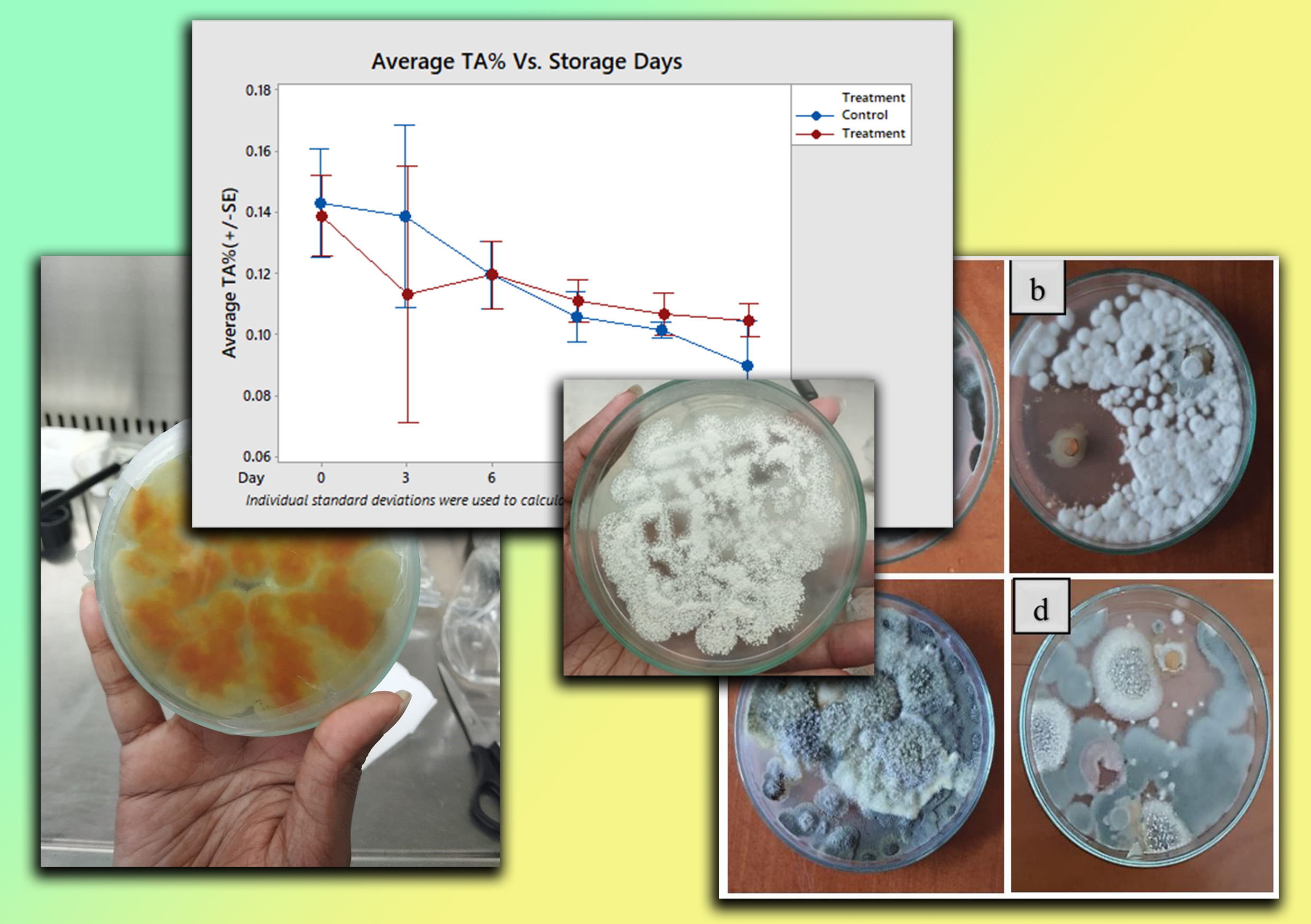
The tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) is the second most extensively cultivated crop globally. However, an estimated 25% to 42% of the worldwide tomato yield is lost during the post-harvest stage, primarily due to various factors, including pathogen infections. Especially, Penicillium species are a significant cause of post-harvest losses, particularly under refrigerated storage conditions. Antagonistic yeasts have shown promising potential in controlling fungal pathogens. Therefore, this study focuses on isolating yeasts and evaluating their antagonism against Penicillium sp. to enhance the shelf life of tomatoes. Four yeast strains were isolated from soil and citrus leaves (YS004, YCL001, YCL002, YCL004),and Penicillium sp. was isolated from infected tomatoes. A dual culture assay was conducted to evaluate the antagonistic activities of each yeast strain against Penicillium sp. Three yeast strains had shown significant antagonistic activity against Penicillium sp. (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05), yet only YS004 (68.27 ± 0.33) exceeded the 55% of percent inhibition of radial growth (PIRG). In the in vivo assay, tomatoes treated with YS004 (4.04 × 10-5 cells mL-1) exhibited the lowest disease severity percentage of 45 ± 2.89 and the lowest disease incidence of 43.33 ± 5.77%. The tomatoes treated with YS004 achieved a shelf life of 19 days compared to 12 days for the control samples. Also, tomatoes treated with YS004 showed statistically significant retention of moisture content (p = 0.0000; p < 0.05) and reduced weight loss (p = 0.0000; p < 0.05). A sensory evaluation was done using 30 untrained panellists, and the results indicated that YS004 enhanced the overall acceptability of tomatoes. Therefore, applying the YS004 yeast solution is a promising and effective bio-control agent that can extend the shelf life of tomatoes by controlling the Penicillium pathogen in refrigerated conditions.
Keywords: Antagonistic yeast, Penicillium spp., Dual culture assay, Shelf life, In vivo assay