Garlic and Cloves as Promising Antibacterial Agents Against Cariogenic Bacteria- A Mini Review
##plugins.themes.academic_pro.article.main##
Abstract
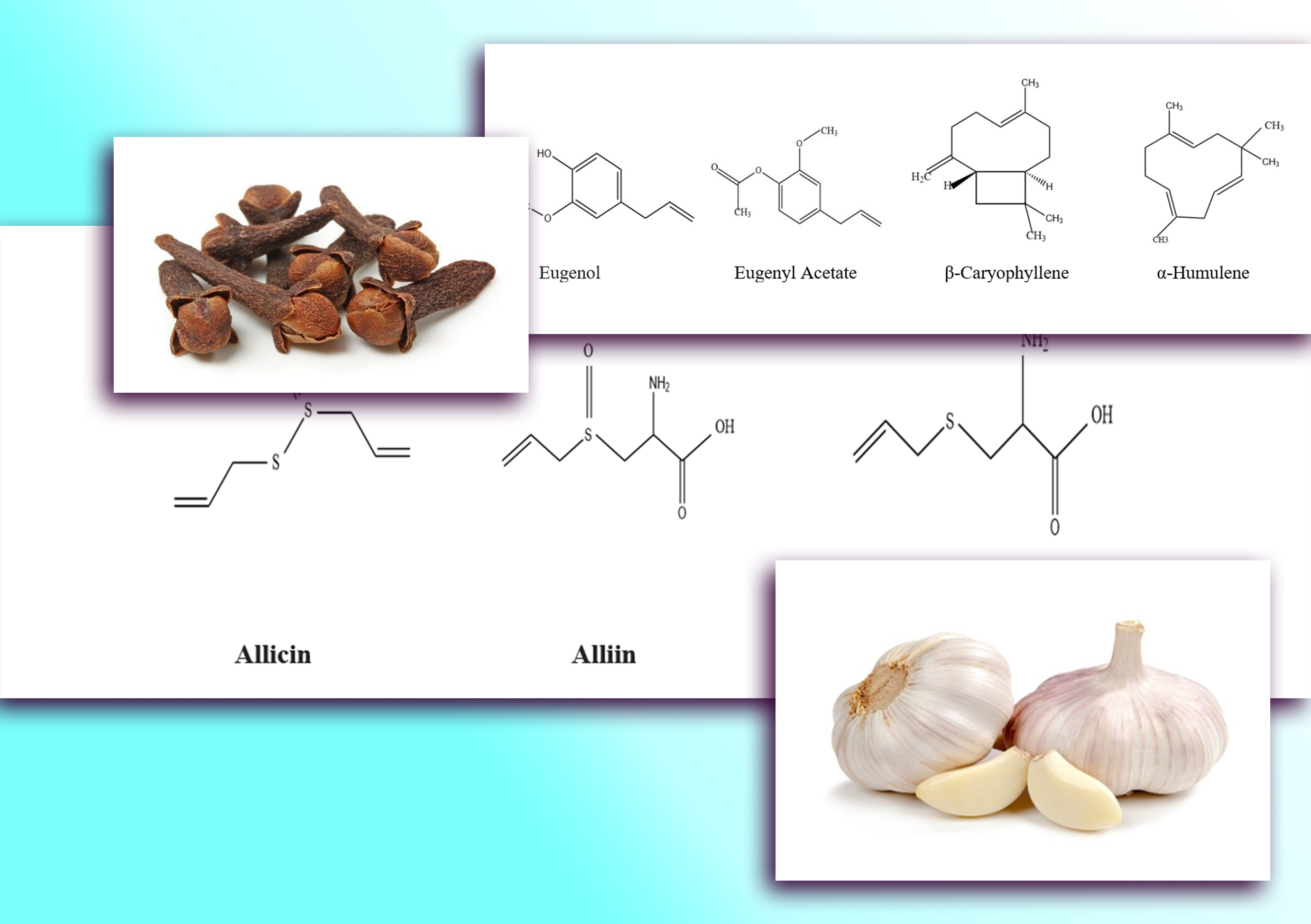
Dental caries is the most common noncommunicable disease in the world. Cariogenic bacteria in the oral cavity such as Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus, cause acid formation, demineralization, and tooth damage by metabolizing carbohydrates. However, many antibacterial agents used in dental caries cause several side effects such as nephritis, eosinophilia and hemolytic anemia, hence it is important to search for some natural-based remedies for the treatment dental caries. Garlic (Allium sativum) is one of the most widely investigated therapeutic plants. It exhibits a wide range of antibacterial activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. due to the presence of a variety of organosulfur chemicals and biologically active constituents including allicin, allicinase, diallylsulphide etc. Clove (Syzygium aromaticum) is widely used in the medicinal, fragrance, and flavoring sectors due of its broad variety of pharmacological and biological effects. The essential oil extracted from clove is used in dentistry as it has ability to relieves pain. Mainly due to the presence of eugenol. The essential oil of cloves exhibited strong antibacterial activity against cariogenic bacteria. Via the destruction of cell walls and membranes, followed by the loss of essential intracellular components, which ultimately leads to bacterial death. The present review mainly aims to discuss the potential ability of garlic (Allium sativum) and cloves (Syzygium aromaticum) to activate different antibacterial mechanisms against cariogenic bacteria.
Key words; Cariogenic bacteria, Garlic (Allium sativum), Clove (Syzygium aromaticum)